There is an inexplicable joy in being outside on a beautiful sunny day! Lying on the beach, soaking up the sun and sipping an ice cold drink – it just feels perfect. But sun exposure can be harmful to your skin as you age, causing a phenomenon known as sun damaged skin. What is this exactly? Is there a way to prevent this? Keep reading this article and you will find out.
Symptoms of sun damaged skin
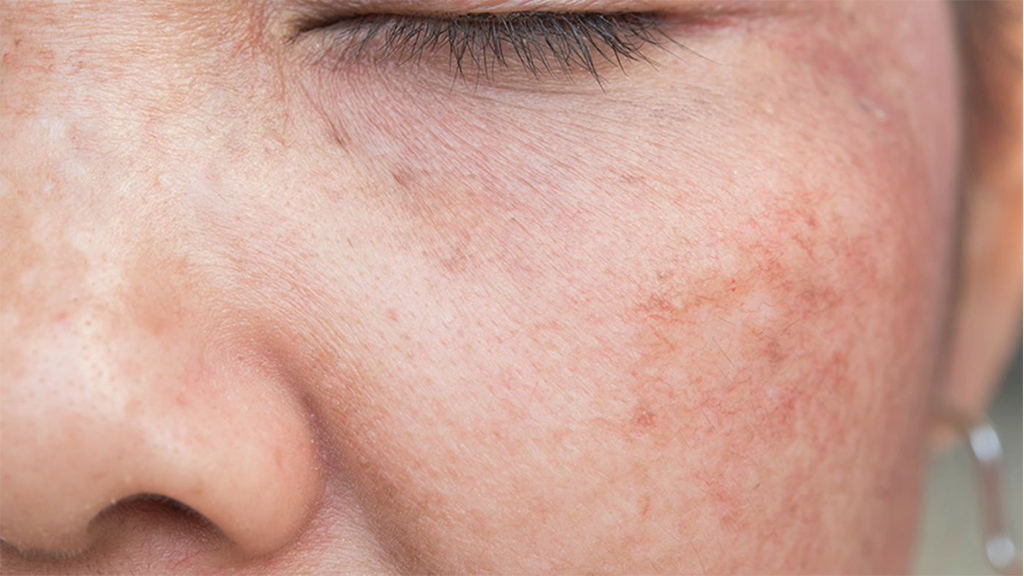
Unlike the chronological aging of your skin caused by age and genetic diseases, photoaging is caused by the severity of UV exposure. Some of the most common symptoms of sun damaged skin are (1):
wrinkling of the skin
Skin pigmentation leading to the development of sun spots and liver spots
freckles on the skin
dryness and roughness of the skin
loss of skin elasticity
If you notice any of these symptoms, chances are your skin is sun damaged. But who is more prone to sunburn or sun damaged skin? Find out in the next section.
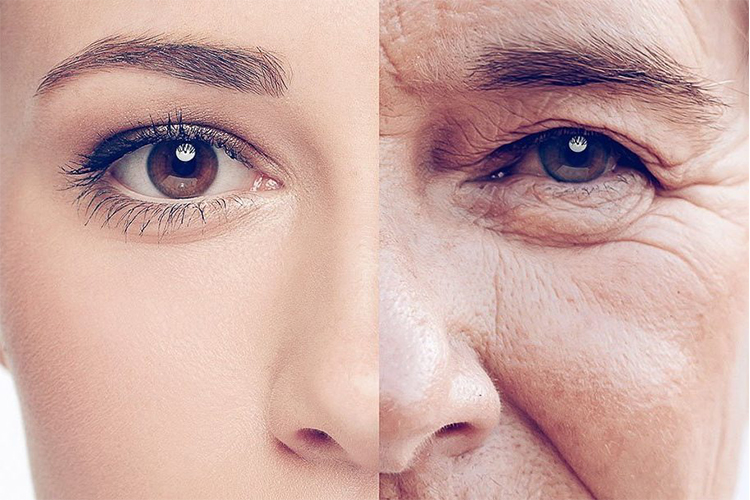

Who is susceptible to photoaging?
Research suggests that anyone exposed to the sun is susceptible to photoaging (3). However, a study designed to examine whether a certain demographic is more susceptible to sun damage found something interesting. It has been shown that people with fair skin, especially fair-skinned men, are more likely to suffer from severe photoaging of the skin (4).
However, if your skin is sun damaged, what can you do about it? Or is it even reversible? let’s find out
How to fix sun damaged skin
When UV rays damage your skin, they can alter your DNA and cause melanoma (a type of skin cancer), which is irreversible (5). Eliminating UV damage on the skin is not easy and requires a lot of time, patience and the use of specialized skin care products. It might or might not work for most people. Here are some products you can try and use against sun damaged skin.
niacinamide
Research suggests that topical application of niacinamide may help reverse the effects of sun damage on the skin. It can help remove fine lines and wrinkles caused by photoaging (6). Niacin, a type of niacinamide, is available as an ingredient in certain serums and creams and is easy to incorporate into your skincare routine.
azelaic acid
Although azelaic acid is commonly used to treat acne, some research suggests that it may also help reverse photoaging of the skin (7). Studies in mice suggest that concentrated forms of azelaic acid may be able to inhibit melanoma cells and reduce the pigmentation they cause (8).
vitamin C
Studies suggest that topical application of vitamin C-based skin care products can reduce and prevent photoaging of your skin. Vitamin C is also known for its photoprotective, antioxidant and anti-aging properties. It can also help improve collagen production and make your skin look younger (9).
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
Research suggests that AHAs may help increase the thickness of your epidermis, making it less susceptible to photoaging and possibly reversing its effects (10). Using sunscreens and creams that contain AHAs or glycolic acid can be added to your skincare routine to reverse the effects of photoaging.

retinoids
Skin care products that contain retinoids can help reverse photoaging of the skin. Research suggests they may be able to reduce the pigmentation that causes dark spots and age spots. Among the various retinoids, tretinoin is considered to be the most effective in reversing the symptoms of photoaging (11).
Getting rid of sun damaged skin must be your last resort. Preventing sun damage or photoaging should be your primary focus. Prevention is better than cure and it’s also cheap. Let’s find out how to prevent sun damage to your skin.
How to protect your skin from sun damage
- It’s easy to protect your skin from sun damage. Follow these simple tips and you’re good to go.
- Daily sunscreen use, regardless of the weather outside, is crucial to protect your skin from sun damage (12). Apply 15-30 minutes before going outside.
- Choose a sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays and has at least SPF 30.
- If you have a toddler at home, it is best to keep them away from bright sunlight as they have very sensitive skin.
- Try to reduce the time you spend in the sun. If possible, avoid exposure to the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., as UV radiation is most intense at this time.
- Wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants minimizes skin exposure to the sun. Wearing dark clothing can also help block out the sun’s harmful rays. Research suggests that colors like navy blue, black, and dark red absorb more UV rays and offer better protection (13). If possible, try to use UV protective clothing for better effect.
- For the head and neck area, you can use scarves or hats to block the sunlight. You can also use photochromic sunglasses or sunglasses with UV protection lenses.
Try these simple tips and you may be protected from the harmful UV rays that damage your skin. However, following these tips every time may not be feasible for everyone. Certain jobs that require hours of exposure to the sun inevitably increase the risk of sun-damaged skin.
Let’s find out when you need medical help for sun damaged skin in the next section.
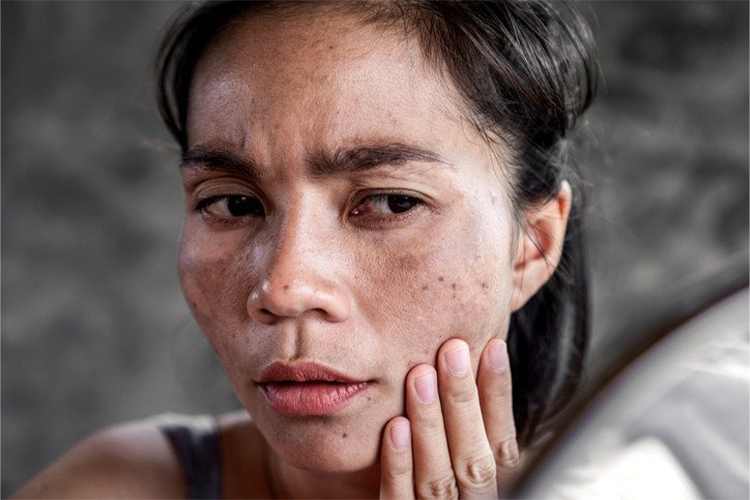

When to see a doctor
Minor symptoms of photoaging like dry skin, fine lines, and wrinkles do not require medical attention. However, in some of the following cases you need to see a doctor or dermatologist.
Actinic keratosis
This is a common skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to UV rays that can progress to squamous cell carcinoma (a type of skin cancer) and other skin problems. These appear as rough, scaly, and bumpy patches near your arms, hands, ears, and neck (14). The treatment of this condition varies from person to person.
Actinic Cheilitis
Similar to actinic keratosis, this skin condition is also caused by exposure to UV rays. Also known as “sailor’s lip,” it often occurs on the lower lip. This is considered a high-risk form of skin cancer and should be diagnosed as early as possible for better management and management (15).
Poikiloderma of Civatte
This is another skin condition caused by prolonged UV exposure that leads to lesions on the skin around the neck. The affected area is itchy and may also cause a burning sensation (16). This condition can be treated with a pulsed dye laser.
In summary, sun damaged skin or photoaging is a result of prolonged exposure to UV rays. Sunspots, freckles and fine lines often appear on the skin as a result of photoaging. Sun damaged skin is unavoidable and inevitable as anyone exposed to sunlight is prone to photoaging skin. However, you can reduce the signs of photoaging by applying sunscreen, wearing long-sleeved clothing, and avoiding the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Excessive sun exposure can cause skin problems like actinic keratosis and actinic cheilitis, which can further progress to skin cancer. In the case of such skin diseases, it is absolutely necessary to be examined by a doctor or dermatologist.